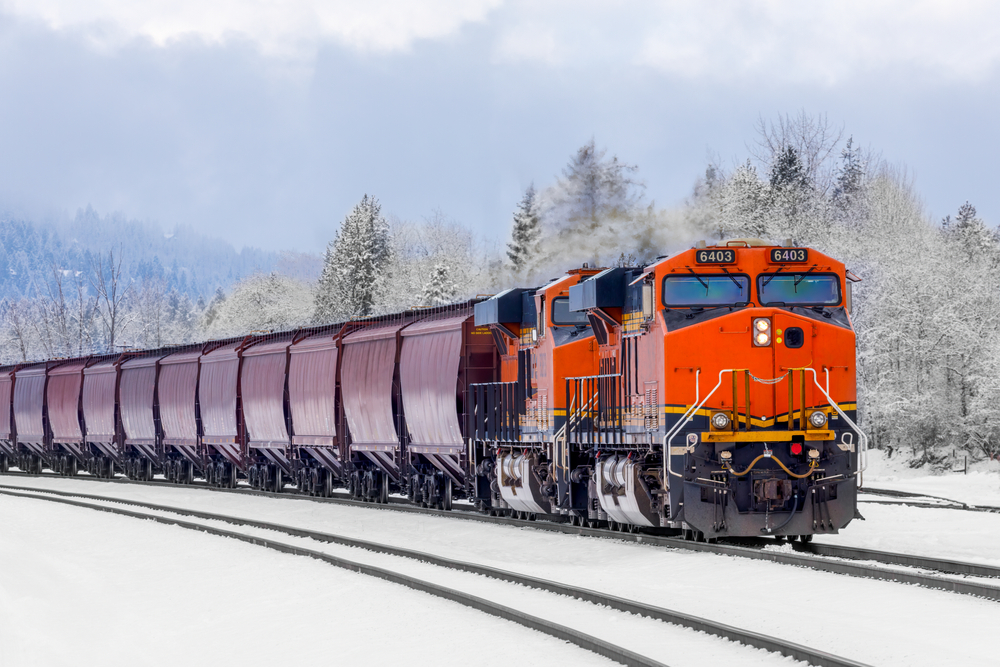
Particularly in nations with large rail systems, locomotives are essential for moving products and people across great distances. Although they live in all kinds of surroundings, winter offers special difficulties with its frigid temperatures and erratic weather. We will look at how winter conditions impact locomotives and what can be done to guarantee they function safely, effectively, and free from problems, all during the colder months.
1. Impact of Cold Temperatures on Locomotive Engines
One of the major difficulties locomotives have in the winter is low temperatures. Like any engine, a locomotive’s engine is vulnerable to the consequences of very low temperatures. The main problem is engine oil becoming thick. Oil becomes more viscous when temperatures decrease, which may cause engine starting trouble and lower efficiency. Furthermore, low temperatures affect the batteries of the locomotive, resulting in slower charging and challenges in sustaining power.
2. Snow and Ice Accumulation
Snowfall may build on the locomotive itself as well as the surrounding track infrastructure. The build-up of snow and ice on undercarriages, wheels, and other parts could compromise locomotive performance. Slower speeds, mechanical breakdowns, and train stuckness resulting from ice accumulation on the tracks all follow from this.
3. Reduced Traction and Slippery Tracks
Apart from the difficulties caused by snowfall, winter conditions may influence locomotive traction as well. Slippery tracks resulting from freezing temperatures may lower the adhesion between the train’s wheels and the rails, therefore affecting locomotive acceleration, deceleration, and control on hills. Wheel slippage, which may create delays and wear and tear on the mechanical components of the train, is another concern it raises.
4. Fuel Efficiency Challenges
Furthermore, difficult to fuel economy in cold weather. Already using a lot of fuel, locomotives can have higher fuel consumption in the cold. This occurs particularly if the engine is having trouble starting or if the cold is thickening the oil; the locomotive’s engine works harder to maintain operating power.
Companies may choose to utilize winterized diesel fuel, which includes additives that stop the fuel from gelling in cold conditions, to lessen these fuel efficiency problems. Given their tendency to operate better in low temperatures, biofuels or alternative fuels might also be considered. Maintaining efficiency also depends critically on frequent fuel checks and maintenance to guarantee the engine is winter-ready.
5. Safety Concerns During Winter Months
Winter conditions raise the possibility of safety events, as low vision, snow, and ice make it challenging for operators to respond quickly to threats. In these difficult circumstances, accidents like derailments and collisions might become more frequent, as the lowered traction and longer reaction times connected with ice tracks and snow-covered components can interfere with safe operations.
6. The Importance of Preventative Maintenance in Winter
Ensuring locomotives run without problems all through the winter depends mostly on preventative maintenance. This covers routine engine, brake, and other important component checks. For instance, making sure the locomotive’s heating system is completely operational helps to avoid the freezing of certain necessary components. Furthermore, crucial is ensuring the fuel is ready for winter and that the lubricating systems are operating as they should.